9. Computational allergenicity prediction of transgenic proteins expressed in genetically modified crops |
Development of genetically modified (GM) crops is on the increase to improve food quality, increase harvest yields, and reduce the dependency on chemical pesticides. Before their release in marketplace, they should be scrutinized for their safety. Several guidelines of different regulatory agencies like ILSI, WHO Codex, OECD, and so on for allergenicity evaluation of transgenics are available and sequence homology analysis is the first test to determine the allergenic potential of inserted proteins. Therefore, to test and validate, 312 allergenic, 100 non-allergenic, and 48 inserted proteins were assessed for sequence similarity using 8-mer, 80-mer, and full FASTA search. On performing sequence homology studies, ~94% the allergenic proteins gave exact matches for 8-mer and 80-mer homology. However, 20 allergenic proteins showed non-allergenic behavior. Out of 100 non-allergenic proteins, seven qualified as allergens. None of the inserted proteins demonstrated allergenic behavior. In order to improve the predictability, proteins showing anomalous behavior were tested by Algpred and ADFS separately. Use of Algpred and ADFS softwares reduced the tendency of false prediction to a great extent (74–78%). In conclusion, routine sequence homology needs to be coupled with some other bioinformatic method like ADFS/Algpred to reduce false allergenicity prediction of novel proteins.
Verma et al.; Immunopharmacology & Immunotoxico-logy; 2011; 33; 410-422. 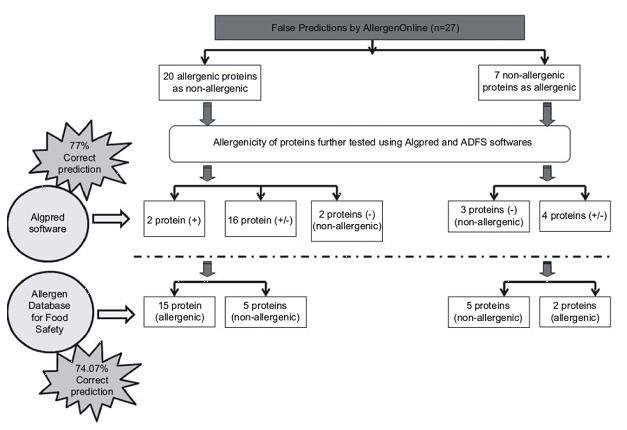 Stepwise summary of Algpred and ADFS analysis of proteins demonstrating anomalous behavior. |